All construction, manufacturing, and repair works utilize stainless steel threaded rods as a fundamental building block. These rods are thick and sturdy because they are made of steel, which makes them very useful and convenient when reliable materials are required. This article presents a complete guide to stainless steel threaded rods, including their materials, several grades and uses, how they are installed, and what to look for when choosing a rod for specific applications. If you are a contractor working on a project that requires adding strength to an entire structure or an engineer attracted to precise assemblies, you will find this guide illuminating in providing the technical details necessary to make the right decisions and maximize project performance.https://ssalloy-steel.com/stainless-steel-rod/
What is a Stainless Steel Threaded Rod, and How is it Used?
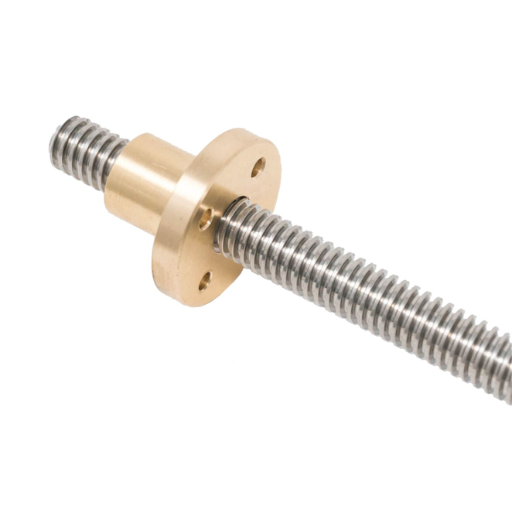

A stainless steel threaded rod is a fastener that resembles a long metal rod with spiral ridges running along its length. Such rods come in various types and grades of stainless steel, commonly the 304 or 316, and have good corrosion resistance, high strength, and durability. Threaded rods find applications in various industries, such as construction, automotive, plumbing, and marine environments. They are mainly used for fastening or reinforcing different parts of the structure to provide strength and alignment. Because of threads, tension is applied evenly in an assembly when several large parts are joined, which helps connect large structures, anchoring systems, and supporting loads in harsh conditions.
Understanding the Thread and Its Importance
Regarding the features of the threaded rods made of stainless steel, namely the threads, I must say that these elements became very significant features of such structural fasteners. The geometry of threads allows a sheer engagement with materials to ensure maximum contact and load flotation. The thread profile, which is made to conform to specific standards like UNC or UNF, is essential to the performance and usability of nuts and other fittings. Threads play a critical role in easing tension to preserve the structure, and if they are subjected to dynamic loads, there will be no loosening. Using the correct classification of threads in terms of their type and size ensures that the rods find application in diverse circumstances, whether in bolting heavy equipment, coupling structural parts, or designing for intense static stresses. These technical features help me decide to optimally improve my assemblies’ performance and life span and secure their designs.
Common Applications of Stainless Steel Threaded Rods
Stainless steel threaded rods have versatile applications across various industries due to their intrinsic corrosion resistance properties, high tensile strength, and durability. Indicates several key areas where these rods are predominantly employed:
- Construction and Infrastructure: These rods support structural applications such as foundation anchors, connecting beams, and concrete reinforcement. Their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions makes them ideal for use in bridges, towers, and building frameworks.
- Automotive and Machinery: In this sector, threaded rods assemble and secure components such as engines, gearboxes, and suspension systems. Their precise threading enables secure fastening, which is essential for maintaining alignment and stability under mechanical stress.
- Plumbing and Marine Applications: Due to their excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals, stainless steel threaded rods are frequently employed in plumbing installations and marine settings, where they mount systems and anchor fixtures in corrosive environments.
Technical parameters of significance include selecting the correct grade, such as 304 or 316 stainless steel, each offering differing levels of corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Diameter and thread specification (UNC or UNF) is critical; for instance, a 3/8″-16 UNC rod might be chosen for general construction due to its balanced load-bearing capacity and thread pitch, while finer threads might suit more precise applications.
By aligning project-specific requirements with these parameters, engineers and contractors can ensure that using stainless steel threaded rods maximizes structural integrity and longevity.
Advantages of Using Stainless Steel in Construction
In my opinion, applying stainless steel in construction entails various advantages that significantly enhance the overall effectiveness of the projects. To begin with, its remarkable durability allows structures to perform even in the most challenging environments, which is why I always consider stainless steel for long-lasting and minimal upkeep projects. As a material, its high tensile strength ensures that substantial loads will be borne, thus making it appropriate for primary load-bearing parts. Moreover, stainless steel’s workability and attractive appearance, combined with its fire and heat resistance, make the material suitable for most architectural forms, contributing to the safety of the construction.
Regarding stainless steel, specific technical details must be analyzed in a particular grade, most often 304 or 316, in which case 316 is recommended in marine or other chemically aggressive environments. It is important to note that the type of alloy and its finish directly affect the metal’s usability on certain surfaces, hence increasing the structural security and durability. In this way, I make sure that applying these alloys in buildings and constructions is efficient and productive in a range of projects when I consider all these components.https://ssalloy-steel.com/blog/common-steel-alloys/
How to Choose the Right 304 Stainless Steel Threaded Rod for Your Needs
Numerous factors must be considered when picking the correct threaded stainless steel rod made of 304. First, consider how the rod will be used; although it is made of 304 stainless steel, which has excellent corrosion resistance, it can also be unsuitable for certain highly corrosive situations. The appropriate mechanical strength for the use ought to be determined to be safe, and the rod’s sufficient tensile strength should be able to support the load it will carry. The thread size and pitch used should help synergize with all other interdependent components of the assembly structure to ensure adequate tension is applied. Also, any regulatory or international standards that the rod in question has to meet, such as ASTM or ISO, ought to make them conform to the expectations for the project and industry standards. With such successive consideration of the above factors, a perfect 304 stainless steel threaded rod that meets structural design and application requirements will be made.
Determining the Correct Length and Size
To establish a proper length and size for a threaded rod made of stainless steel, I evaluate the design and environmental parameters that my work requires. First, I establish precisely how long the rod has to be, including any needed anchorage depth and any possible variances that may occur during fitting. Secondly, I check that the diameter thickness is adequate for the loads to be carried by tensile stress specifications given in publications. Referring to these parameters and the standards set by ASTM or ISO, I will have no reservations about the rod because it will safely fulfill the physical requirements of the application and will not interfere with the other components of the assembly.
Evaluating Corrosion Resistance in Different Environments
Several significant factors should be considered when determining the corrosion resistance of stainless steel threaded rods in various environmental conditions. The steel grade number is the most critical parameter since it determines the corrosion resistance. Take 304-grade steel, for instance, for less corrosive environments. However, the steel is not suitable in extreme or corrosive marine environments. For these environments, 316-grade stainless steel is more ideal as it has more resistance to chlorides and seawater.
In addition, please evaluate the corrosive agents that are prone to be present and their concentrations, for example, acids or alkaline agents, which will influence the material used. Other parameters, such as environmental temperature and humidity, should also be considered as they affect the corrosion rate. For instance, an increase in temperature almost always results in an increased corrosion rate, meaning that materials of higher alloy content and more robust coatings would be necessary.
Passivation and surface finishes can also be classified as significant technical parameters that influence the corrosion-resistance characteristics. Such further passes in the selection of a rod mean that the coating or treatment used on the rod is appropriate to prevent corrosive processes. After adequately reviewing these parameters, the most suitable grade for stainless threaded rods shall be selected, which will perform in harsh environments without losing strength.
Selecting Between 304 and 316 Stainless Steel
Understanding both alloys’ disparities and strengths is vital in understanding which to pursue. A project that does not need the qualities offered by 304 and 316 stainless steel hardly exists. Since 304 and 316 stainless steels are austenitic alloys, their constituent elements, Chromium, Nickel, and Carbon, can generally be said to be the same. The difference, however, lies in adding Molybdenum to the 316 stainless steel, which enhances its corrosion resistance, especially in the presence of chlorides and saline environments. With this enhancement, 316 steel is best suited for marine, chemical, and high saline environments as it is more durable and has greater pitting and crevice corrosion resistance.
In such situations, even the low price of 316 does not seem to help, and 304 stainless steel becomes the only option available as it is less expensive and has sufficient corrosion resistance for most applications that do not have exposure to certain harsh chlorides. 304 is an excellent possibility for projects that do not need attributes offered by the 316. Regarding mechanical characteristics, the tensile strength of both grades may be almost the same, with 304 having the edge in formability and weldability.
When choosing between 304 and 316 stainless steel, the evaluator must also factor in the surrounding climate, the financial aspects, and the mechanical parameters of the application. As for choosing the right type of stainless steel for your structure and for a specific environment, this selection may also benefit from looking through in-depth technical datasheets and specifications readily available on websites such as MatWeb, Corrosion Materials, and the Stainless Steel Information Center.
What are the Different Types of Threads and Their Uses?

Threaded rods are used in a wide range of applications, and thus, several thread types have been developed to suit various load and environmental requirements. The thread types have been coined as coarse, fine, acme, and metric threads. They contrast coarse threads with a shallow depth with their peaks and troughs widely apart, making fastening and unfastening easier and quicker, thus suitable for broader applications. Fine threads are effective for applications like bolts where more significant resistance to tensile forces is required since the distance between the threads, including barring, is short. Acme threads are shaped like trapezium and are widely used for screwers because of their more robust construction and lower friction. They are also known as lead screws. While the above two are particular applications, the latter includes the most universally accepted dimensions; hence, it can be applied to other parts without bother. When asking the type of threads to choose, one has to consider the application’s needs, particularly the load it has to wear, its assembly features, and compatibility with the system into which it will be incorporated.
Understanding Coarse vs. Fine Threads
As I discuss the distinction between coarse and fine threads, I am talking about their definitions as well as areas of application. Coarse threads are mainly applied where easy assembly and higher tolerance damage are necessary. These are less likely to be cross-threaded and serve well under instances of quick assembly. Because of their greater area of external radial, fine threads are more resistant to tensile breakage, making them appropriate in locations requiring high precision and vibration resistance. In logo design, when I need to choose one between them, I consider the design specifications of my project together with the opportunities that will be encountered in practice – and such insight seems to me to be provided by Grainger for mechanical issues, McMaster-Carr for standards regarding the hardware and Fastenal for advice about specific applications.
Exploring TPI (Threads Per Inch) and Its Impact
Threads Per Inch (TPI) is a critical specification in threaded components, significantly affecting mechanical performance and compatibility. TPI denotes the number of thread crests per inch and influences thread engagement, fastener grip, and load distribution. A higher TPI signifies finer threads, which provide greater grip strength and are advantageous in precision applications prone to vibrations. Conversely, a lower TPI, indicative of coarser threads, supports faster assembly and greater resilience against impacts.
When selecting TPI, the corresponding technical parameters include:
- Load Requirements: Coarse threads handle larger loads more efficiently, while fine threads are ideal for precise load applications.
- Material Hardness: Finer threads are suitable for more complex materials, and they have a solid grip to prevent loosening under vibration.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider conditions like moisture and corrosion; finer threads with increased contact area may enhance sealing capabilities.
- Assembly Speed: Coarser threads allow quicker assembly and disassembly, making them preferable in non-precision applications with frequent adjustments.
- Compatibility with Existing Components: Ensure that the TPI matches the existing components to avoid mismatches that can lead to equipment failure.
Combining TPI considerations with load requirements and material properties can achieve optimal performance, ensuring mechanical integrity and operational efficiency across various applications.
How to Properly Install and Use Threaded Rod 304 Stainless Steel

To enhance their performance and maintain structural integrity, 304 stainless steel threaded rods must be properly installed and utilized. Commence by identifying the appropriate rod dimensions and threads for the operational loads needed and, with the aid of the component, ease of operational fitting. When installing the threaded rod, use the appropriate tools to apply the proper torque and avoid damage to the threads due to over-tightening. Dismantle the assemblies and clean the rods to prevent scratching of the threads during engagement and ensure enough friction for the assemblies. For applications with dynamic loads or vibrations, make sure to use lock nuts or thread-locking compounds to help maintain the position of the parts. In addition, all industry expectations and guidelines, especially on safety issues during assembly applications, must be observed. Regular check-ups and maintenance are encouraged so that, if the rod is already in use, there will be an examination of the size, corrosion, or mechanical damage, and the installation can then be reiterated without any compromise of reliability in the future.
Steps for Cutting and Finishing Threads
Cutting and finishing threads require precision and adherence to best practices to ensure optimal performance and compatibility. Here, based on insights from industry leaders , is a concise guide to achieving high-quality threaded components:
- Selection of Tools and Materials: Choose the appropriate tapping and die set compatible with your material. High-speed steel (HSS) taps and dies are preferred for their durability and precision when cutting threads on metals.
- Preparation of the Material: Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped to prevent movement. Mark the starting point for your threads, and use a center punch to create an indentation, guiding the tap or die for accurate cutting.
- Thread Cutting Process:
- Tapping: To create internal threads, a tap wrench will rotate the tap clockwise into the pre-drilled hole. Apply consistent pressure and periodically reverse counterclockwise to clear the cut material.
- Using a Die: External threads can be cut by threading a die onto the end of a rod, turning clockwise with a die stock. Reverse intermittently to break and remove chips.
- Lubrication: Apply cutting oil or suitable lubricant to reduce friction and heat buildup, ensuring smoother cuts and extending tool life.
- Finishing the Threads: Once the threads are cut, inspect them for uniformity and burrs. Use a thread file or fine-grit sandpaper to remove excess material for a clean finish.
- Verification and Quality Control: Measure the threads with a thread pitch gauge and verify with a ring gauge or caliper to ensure adherence to specification standards. Confirm compatibility with corresponding components.
Technical Parameters:
- Drill Size: Select the correct drill size for the hole to be tapped. This is generally recommended in tapping charts specific to thread size and material.
- Thread Pitch: Align with industry-standard pitches for compatibility; for instance, a standard metric pitch might be M8x1.25.
- Torque Settings: Following manufacturer guidelines on tool torque during tapping to avoid damage.
Adhering to these steps and parameters assures precision and integrity in thread creation, resulting in reliable and efficient threaded components suitable for diverse applications.
Best Practices for Securing with Nuts and Bolts
Based on my experience and the material I trust, it is possible to outline particular best benchmarking practices when the components are secured with nuts and bolts to achieve the best performance. First, fasteners should always be selected according to the application load and required environmental conditions. For example, it is appropriate to use stainless steel in aggressive environments. The holes should be in the proper position, and clean thread areas on the nut and the bolt should be ensured to avoid mismatching threads during mesh. The manufacturer’s specific torque should be controlled with a torque wrench; this is sufficient to keep the correct tension without excessive tightening. It is good practice not to use deteriorated bolts since they may lose some structural properties of the assembly. Besides, the use of washers can be helpful to ensure that the localized pressure and surface finishes are not weathered or damaged. For applications that may encounter vibration, nylon or thread locks can be used to stop the joint from loosening. These include bolt grade, the distance between each thread pitch, and twist knot parameters. These must fit the materials and design features for a firm and dependable bond. If the practices are followed, you are guaranteed sturdy and robust assemblies for any application.
Ensuring Safety and Stability in Hangers and U-bolts
As far as I am concerned, taking precautions and stabilizing hangers and U-bolts involves multiple essential steps. To begin with, choosing the appropriate size and kind of hanger and U-bolt is crucial, considering the load and environmental conditions, to avoid failure. Other specifications, such as material grade or corrosion resistance, should also be examined; stainless steel types are the most appropriate in corrosive conditions. The members must be aligned and spaced correctly to eliminate the risk of uneven distribution of loads, leading to mechanical stress and possible damage to the assembly. Although there are different means of installing bolts, calibrated torque wrenches can be used to minimize the loosening of bolts, which often occurs in dynamic conditions. Lock washers or glue can also be used to enhance the assembly’s security wherever appropriate. Other than that, the assembly must be inspected and repaired regularly. Search for exhaustion and these other deformations and remedy the situation to aid the existence of the structure. By implementing these best practices, the everyday working life of the elements used in constructions with hangers and U-bolts is sufficiently increased by the best practices of the leading manufacturers around the industry.
Where to Shop and How to Get the Best Price on Stainless Steel Threaded Rods

Any utilization of a threaded rod made of stainless steel would require the user to consider various procurement points for the best price and best stock availability. Platforms like Amazon and eBay and industrial supplier sources like Grainger or McMaster-Carr have plenty of good options and recommendations from others who have purchased them. Supplies for the construction and hardware industry help get what is required very fast, and most of the time, the customers can see what they are buying. To offset costs effectively, placing a bulk order with wholesalers or manufacturers is advisable, especially during large-scale projects. Visiting various websites to look at other deals and offers from the market can help a lot with copious savings. Also, I reached out to the end suppliers and did what was required to get the most appropriate specification of stainless steel threaded rods at the lowest price possible.
Comparing Prices Across Different Suppliers
To effectively compare prices across different suppliers for stainless steel threaded rods, it is essential to consider both the cost and the associated technical specifications. Here are some strategies and parameters to guide the comparison:
- Specification Matching: Ensure the products match specifications, including diameter, length, thread pitch, and material grade (e.g., 304 vs. 316 stainless steel). Discrepancies in specifications can lead to variations in price and performance.
- Total Cost Consideration: In addition to the base price of the rods, factor in additional costs such as shipping, taxes, and potential bulk discounts. Some suppliers may offer reduced rates for large orders or free shipping, which can impact the overall expense.
- Supplier Reputation and Reliability: Investigate supplier reviews and ratings. A lower price might not always reflect the best option if the supplier has poor reliability or a history of product inconsistency.
- Lead Time and Availability: Consider the product’s availability and lead time. Suppliers with faster delivery times or in-stock items can be crucial, especially for projects with tight schedules.
- Technical Parameters for Equivalency:
- Thread Standard Compliance: Verify compliance with standards such as ISO or ASTM for uniform quality.
- Corrosion Resistance: Evaluate based on environmental conditions, requiring specific grades for durability.
- Mechanical Properties: Confirm tensile strength and hardness ratings to ensure suitability for the intended application.
By systematically evaluating these factors, one can achieve a comprehensive comparison, ensuring the procurement of stainless steel threaded rods that are cost-effective without compromising on quality and project requirements.
Understanding the Shipping and Handling Process
It became clear that an effective shipping system is essential in preserving the quality of products and resulting in customer satisfaction. To begin with, the logistics of the processes, such as packaging, labeling, and moving, need to be appreciated. I have discovered that customer experience is frequently a matter of choosing a fast and trustworthy courier service. The shipper and the receiver require up-to-date information, making tracking an essential shipping component. I seek to reduce the impact of handling by employing standard warehouse management procedures to ensure that items are secured, collected, and packed efficiently and securely. In this way, I could guarantee a good shipping service by monitoring the progress of these processes and their improvement concerning developed practices in the field and consumers’ views.
Exploring Custom Options for Unique Projects
In exploring custom options for unique projects, I have found that tailoring stainless steel threaded rods to meet specific project needs requires a nuanced approach. I gained insights into customizing dimensions, materials, and finishes by examining leading sources such as Fastenal, Threaded Rod Supply, and U-Bolt-It. Fastenal offers an intuitive customization process that facilitates the selection of specific grades, such as 304 or 316 stainless steel, providing solutions designed to handle diverse environmental stresses. Threaded Rod Supply emphasizes precision in cuts and threading, ensuring compatibility with specific design parameters. Meanwhile, U-Bolt-It allows adjustments in diameter and length, catering to non-standard applications where exact measurements are paramount. Utilizing these resources will enable me to specify custom rods that align perfectly with project specifications, optimizing performance and durability in demanding environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a stainless steel threaded rod, and how is it commonly used?
A: A stainless steel threaded rod is a fastener that is fully threaded along its length. It is commonly used in construction, machinery, and furniture assembly as an anchor bolt or threaded stud. This product is known for its corrosion-resistant properties, making it suitable for indoor and outdoor use.
Q: What materials are stainless steel threaded rods made from?
A: Stainless steel threaded rods are typically made from 18-8 stainless steel or 316 stainless steel. These materials are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and strength, making them ideal for various applications, including marine and chemical environments.
Q: What lengths and diameters do stainless steel threaded rods offer?
A: Stainless steel threaded rods are available in various lengths and diameters to suit different project needs. Standard lengths can range from 36 inches to longer, while diameters may vary depending on the project’s specific requirements.
Q: Are stainless steel threaded rods suitable for outdoor use?
A: Yes, stainless steel threaded rods are corrosion-resistant and suitable for outdoor use. They are ideal for moist environments, such as gardens or saltwater applications, because they resist rust and other corrosive elements.
Q: What is the difference between 18-8 stainless steel and 316 stainless steel threaded rods?
A: 18-8 stainless steel threaded rods are made from a standard grade of stainless steel with good corrosion resistance and strength. 316 stainless steel threaded rods offer even higher corrosion resistance, especially in saltwater and chemical environments, making them suitable for more demanding conditions.
Q: Can stainless steel threaded rods be used with stainless steel hex nuts?
A: Yes, stainless steel threaded rods are commonly used with stainless steel hex nuts to create a reliable and robust fastening system. The combination provides excellent corrosion resistance and strength for a variety of applications.
Q: What are some typical applications for stainless steel threaded rods?
A: Stainless steel threaded rods are versatile and commonly used in construction, furniture assembly, machinery, and garden structures. They are often used as anchor bolts, clamps, and threaded studs in various hardware installations.
Q: How do I choose the right stainless steel threaded rod for my project?
A: When selecting a stainless steel threaded rod, consider the environmental conditions, load requirements, and compatibility with other hardware. Choose the appropriate material, such as 18-8 or 316 stainless steel, and ensure the correct length and diameter for your specific application.
Q: Can stainless steel threaded rods be used in corrosive environments?
A: Yes, stainless steel threaded rods are designed for corrosive environments. They provide excellent resistance to rust and chemical exposure, making them suitable for marine, chemical, and outdoor applications.